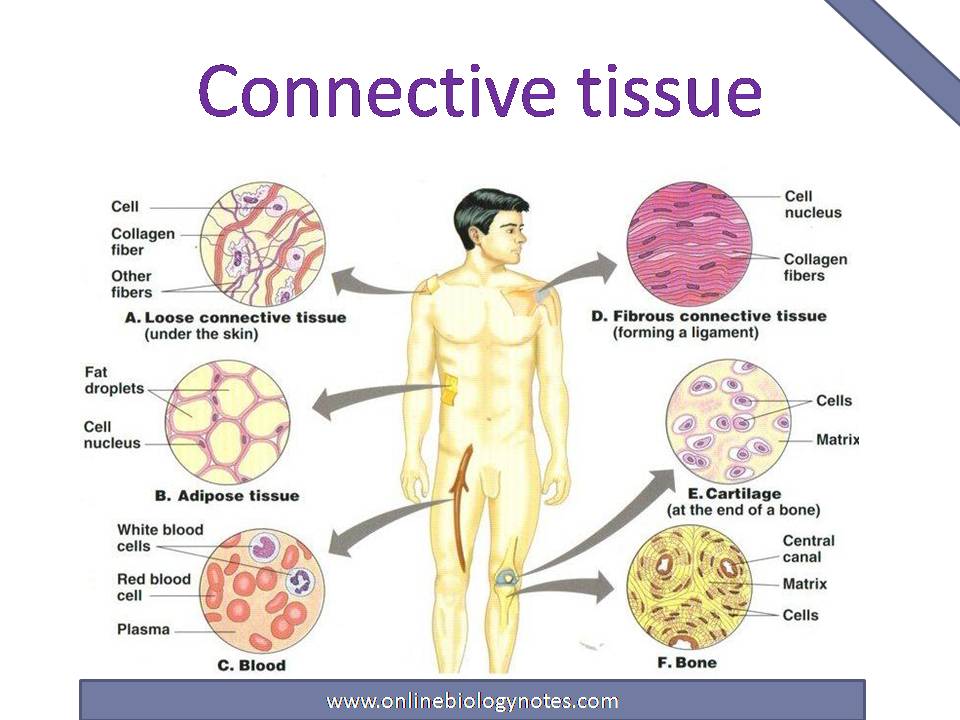
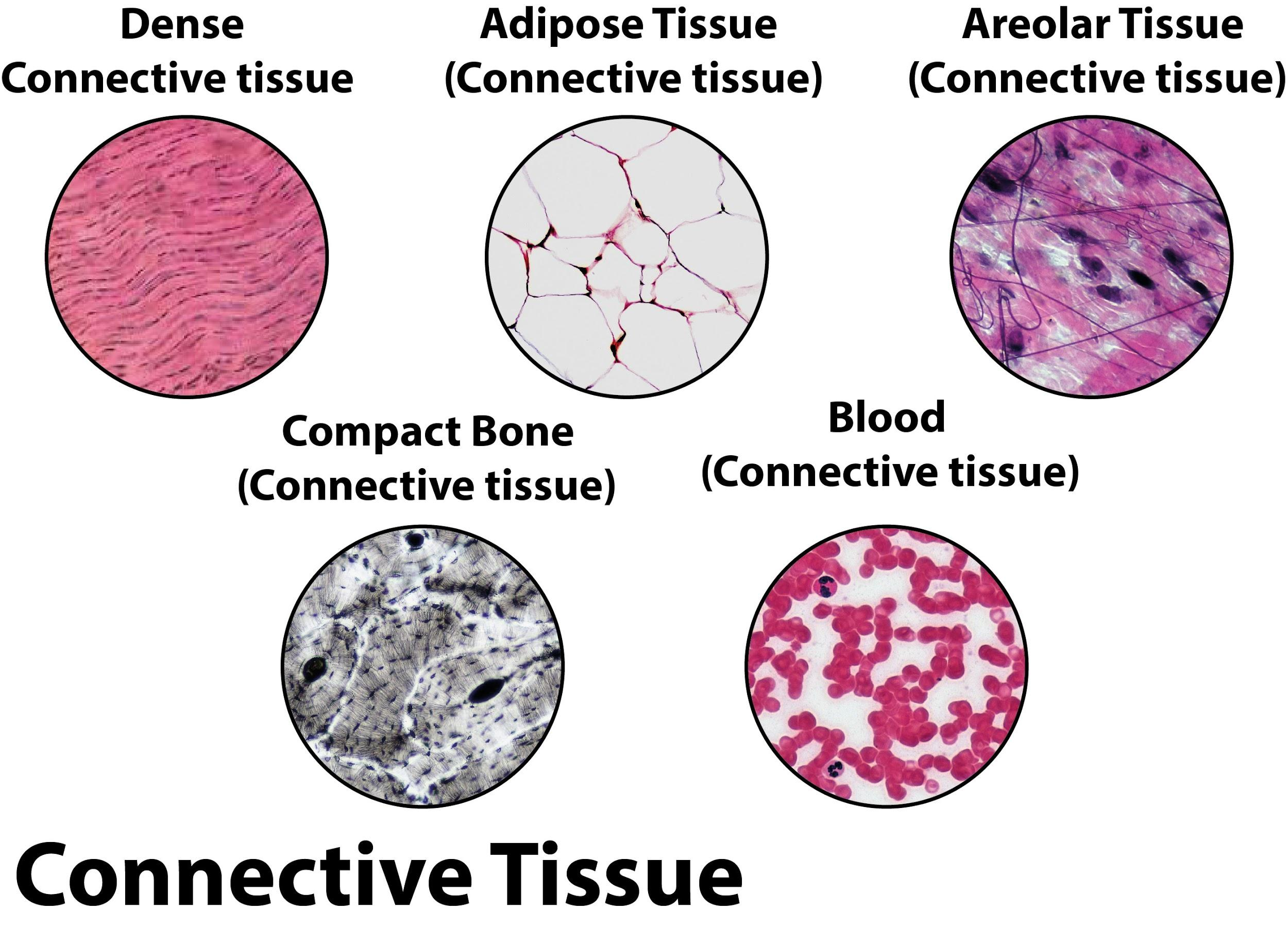
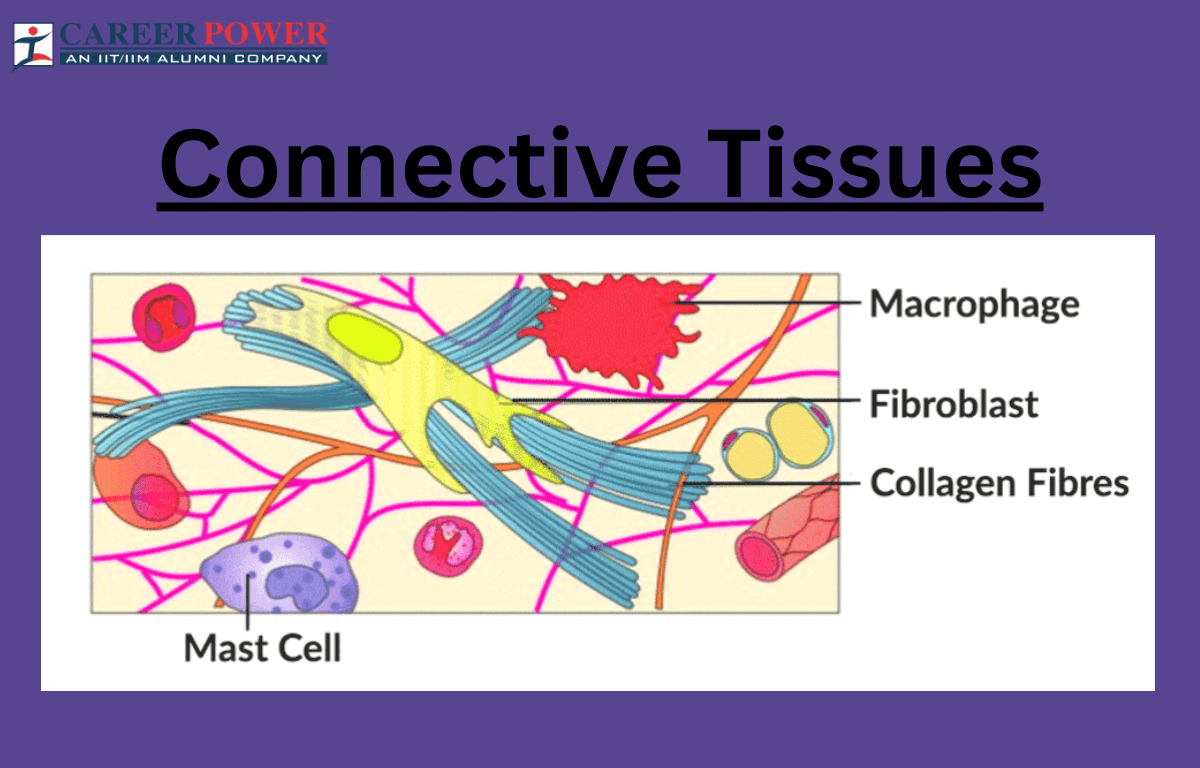
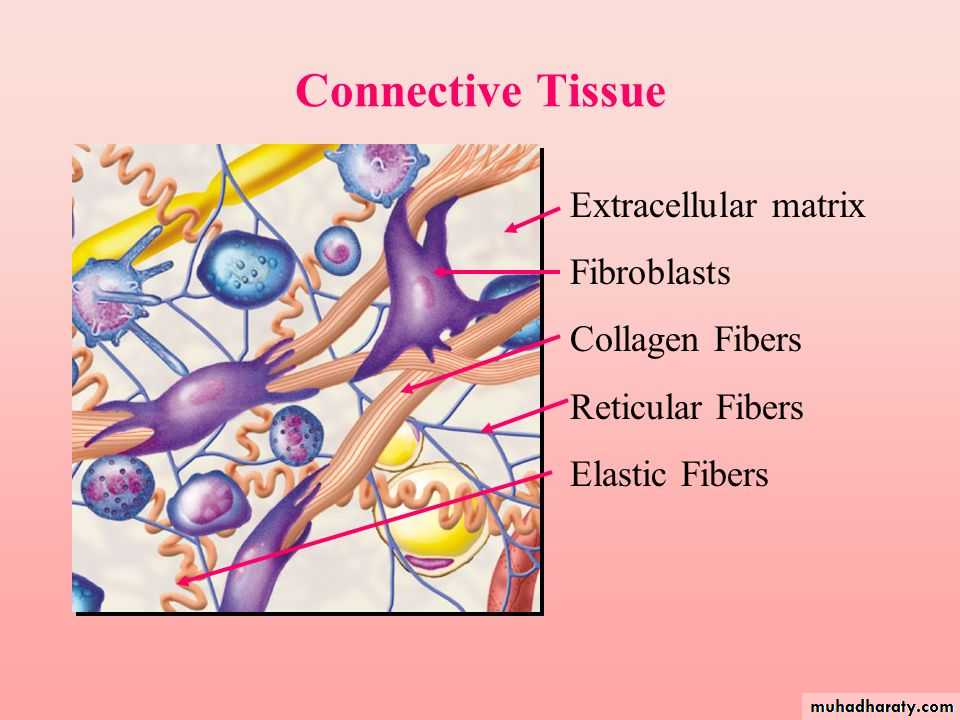
Connective Tissue Function
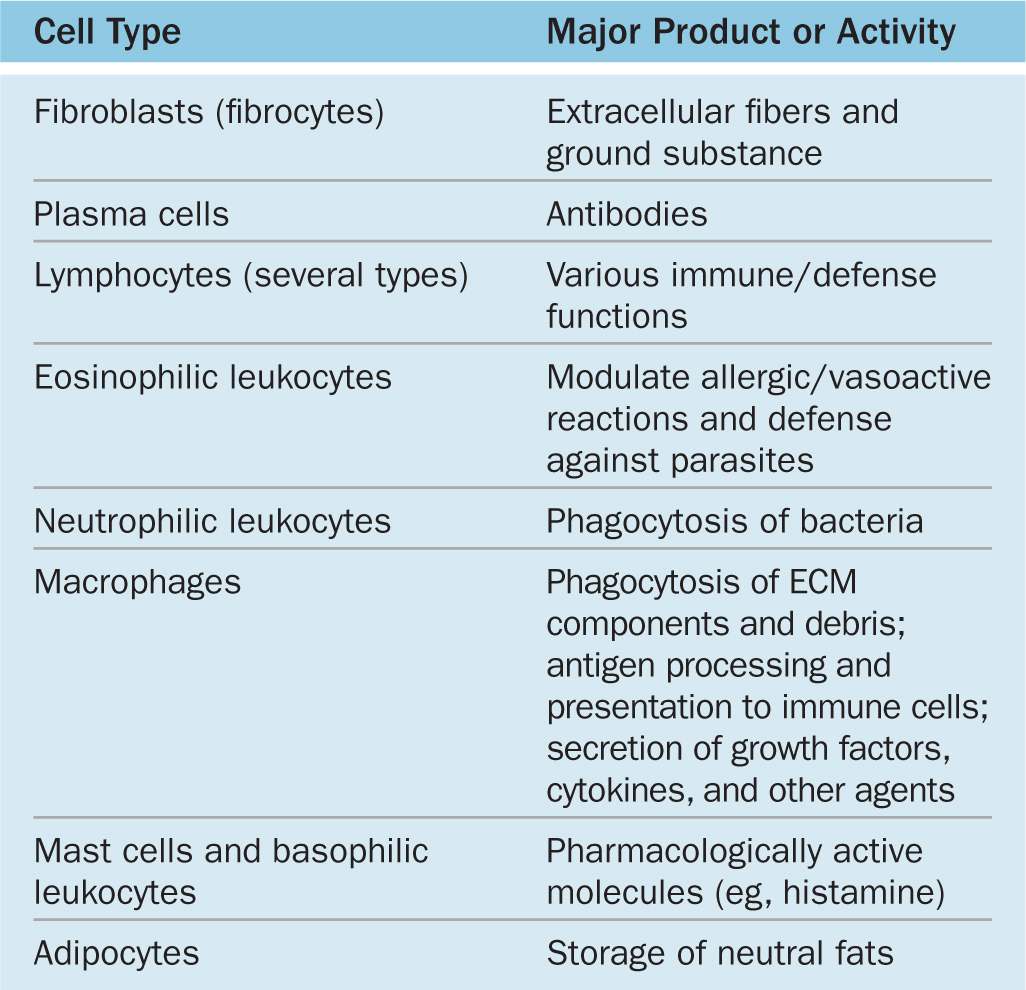
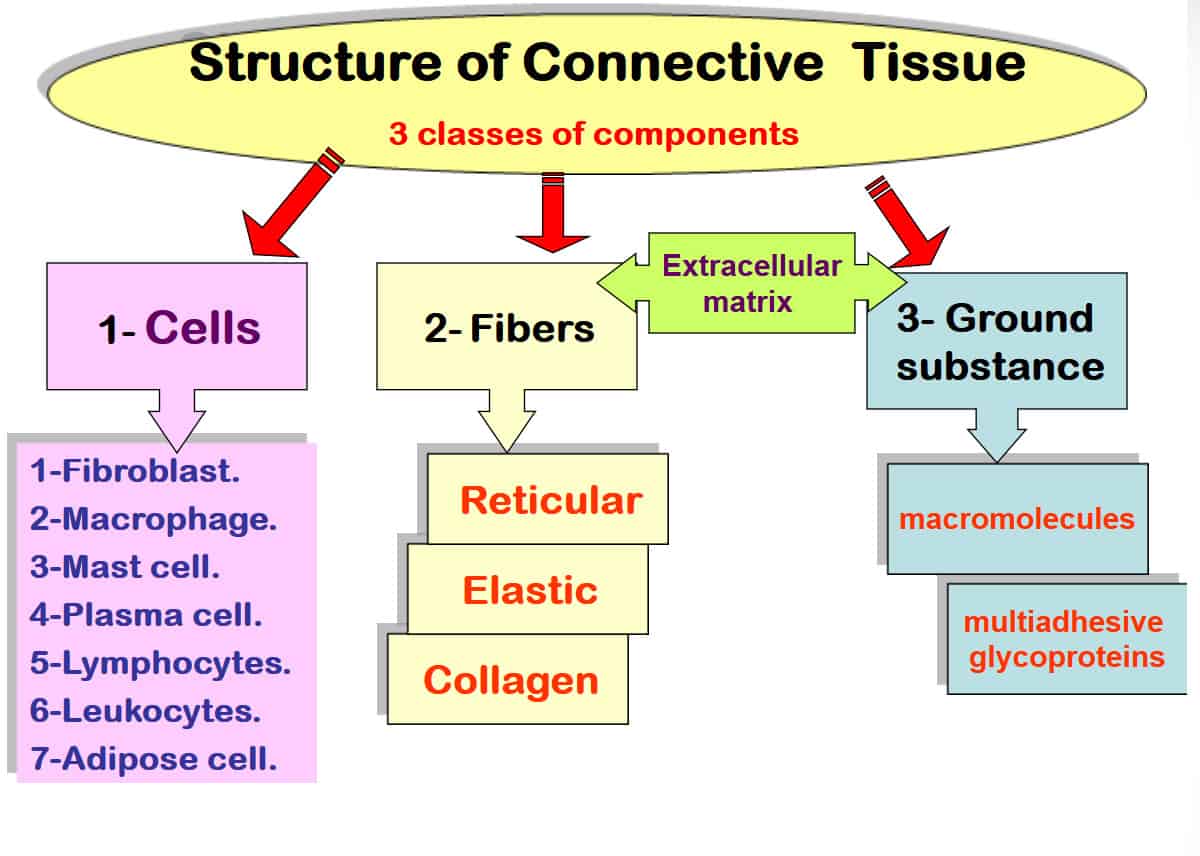
Connective Tissue Function - All nutrient materials and waste products exchanged between the organs and the blood must traverse perivascular spaces occupied by connective tissue. Cartilage is a form of connective tissue in which the ground substance is abundant and of a firmly gelated consistency that endows this. Connective tissue, tissue in the body that maintains the form of the body and its organs and provides cohesion and internal support, including bone, ligaments, tendons, cartilage, adipose tissue, and. The cells of connective tissue include two types that are relatively stationary—fibroblasts and adipose cells—and several types of motile migrating cells—mast cells, macrophages,.
The cells of connective tissue include two types that are relatively stationary—fibroblasts and adipose cells—and several types of motile migrating cells—mast cells, macrophages,. All nutrient materials and waste products exchanged between the organs and the blood must traverse perivascular spaces occupied by connective tissue. Cartilage is a form of connective tissue in which the ground substance is abundant and of a firmly gelated consistency that endows this. Connective tissue, tissue in the body that maintains the form of the body and its organs and provides cohesion and internal support, including bone, ligaments, tendons, cartilage, adipose tissue, and.
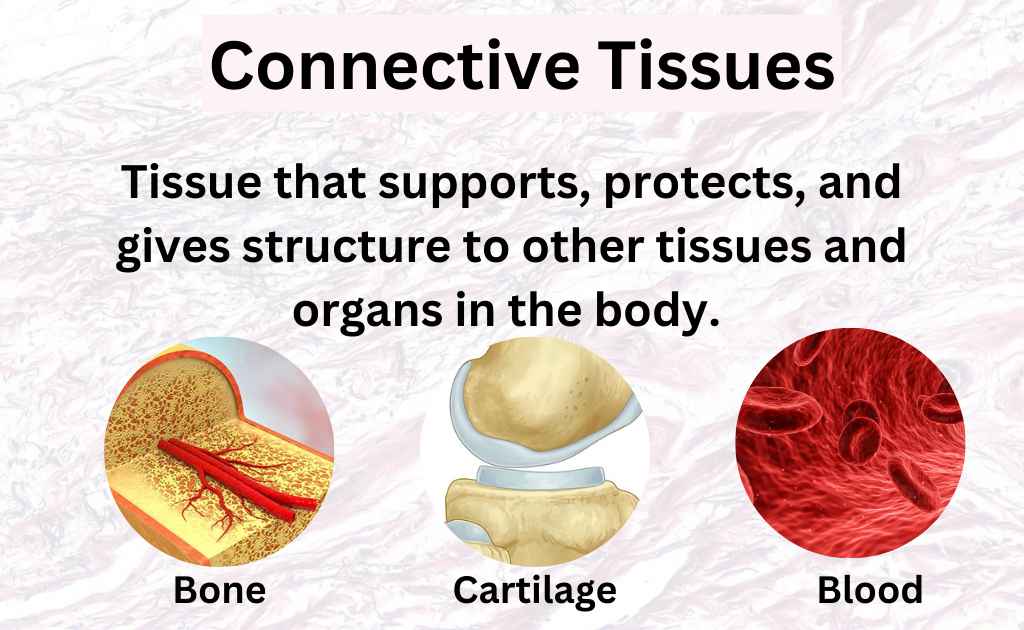
Connective tissue, tissue in the body that maintains the form of the body and its organs and provides cohesion and internal support, including bone, ligaments, tendons, cartilage, adipose tissue, and. The cells of connective tissue include two types that are relatively stationary—fibroblasts and adipose cells—and several types of motile migrating cells—mast cells, macrophages,. All nutrient materials and waste products exchanged between the organs and the blood must traverse perivascular spaces occupied by connective tissue. Cartilage is a form of connective tissue in which the ground substance is abundant and of a firmly gelated consistency that endows this.
Connective tissue characteristics, functions and types Online
All nutrient materials and waste products exchanged between the organs and the blood must traverse perivascular spaces occupied by connective tissue. Cartilage is a form of connective tissue in which the ground substance is abundant and of a firmly gelated consistency that endows this. The cells of connective tissue include two types that are relatively stationary—fibroblasts and adipose cells—and several.
Give the characteristics of connective tissue.
Connective tissue, tissue in the body that maintains the form of the body and its organs and provides cohesion and internal support, including bone, ligaments, tendons, cartilage, adipose tissue, and. The cells of connective tissue include two types that are relatively stationary—fibroblasts and adipose cells—and several types of motile migrating cells—mast cells, macrophages,. All nutrient materials and waste products exchanged.
Connective Tissue Definition, Types, Function and Examples
All nutrient materials and waste products exchanged between the organs and the blood must traverse perivascular spaces occupied by connective tissue. Cartilage is a form of connective tissue in which the ground substance is abundant and of a firmly gelated consistency that endows this. The cells of connective tissue include two types that are relatively stationary—fibroblasts and adipose cells—and several.
Connective tissue pptx D. Talib Muhadharaty
All nutrient materials and waste products exchanged between the organs and the blood must traverse perivascular spaces occupied by connective tissue. Cartilage is a form of connective tissue in which the ground substance is abundant and of a firmly gelated consistency that endows this. The cells of connective tissue include two types that are relatively stationary—fibroblasts and adipose cells—and several.
Connective Tissue Basicmedical Key
Connective tissue, tissue in the body that maintains the form of the body and its organs and provides cohesion and internal support, including bone, ligaments, tendons, cartilage, adipose tissue, and. Cartilage is a form of connective tissue in which the ground substance is abundant and of a firmly gelated consistency that endows this. All nutrient materials and waste products exchanged.
Yoga to your core Connective tissue
The cells of connective tissue include two types that are relatively stationary—fibroblasts and adipose cells—and several types of motile migrating cells—mast cells, macrophages,. Connective tissue, tissue in the body that maintains the form of the body and its organs and provides cohesion and internal support, including bone, ligaments, tendons, cartilage, adipose tissue, and. Cartilage is a form of connective tissue.
Connective TissuesDefinition, Structure, Types, Functions, and Examples
The cells of connective tissue include two types that are relatively stationary—fibroblasts and adipose cells—and several types of motile migrating cells—mast cells, macrophages,. Cartilage is a form of connective tissue in which the ground substance is abundant and of a firmly gelated consistency that endows this. All nutrient materials and waste products exchanged between the organs and the blood must.
Classification of Connective Tissues Anatomy and Physiology JoVe
The cells of connective tissue include two types that are relatively stationary—fibroblasts and adipose cells—and several types of motile migrating cells—mast cells, macrophages,. Connective tissue, tissue in the body that maintains the form of the body and its organs and provides cohesion and internal support, including bone, ligaments, tendons, cartilage, adipose tissue, and. Cartilage is a form of connective tissue.
Connective tissue Tissue biology, Anatomy and physiology, Tissue types
Cartilage is a form of connective tissue in which the ground substance is abundant and of a firmly gelated consistency that endows this. All nutrient materials and waste products exchanged between the organs and the blood must traverse perivascular spaces occupied by connective tissue. Connective tissue, tissue in the body that maintains the form of the body and its organs.
Define Tissue Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
All nutrient materials and waste products exchanged between the organs and the blood must traverse perivascular spaces occupied by connective tissue. Cartilage is a form of connective tissue in which the ground substance is abundant and of a firmly gelated consistency that endows this. The cells of connective tissue include two types that are relatively stationary—fibroblasts and adipose cells—and several.
The Cells Of Connective Tissue Include Two Types That Are Relatively Stationary—Fibroblasts And Adipose Cells—And Several Types Of Motile Migrating Cells—Mast Cells, Macrophages,.
All nutrient materials and waste products exchanged between the organs and the blood must traverse perivascular spaces occupied by connective tissue. Connective tissue, tissue in the body that maintains the form of the body and its organs and provides cohesion and internal support, including bone, ligaments, tendons, cartilage, adipose tissue, and. Cartilage is a form of connective tissue in which the ground substance is abundant and of a firmly gelated consistency that endows this.