Faraday S Law Integral Form
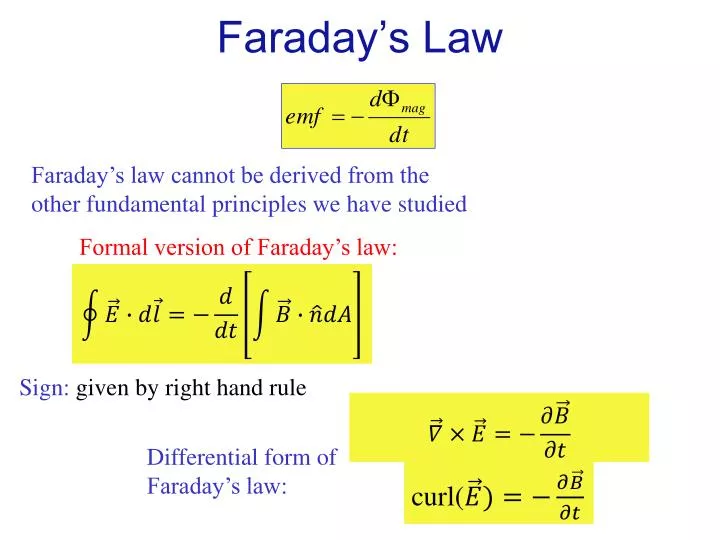
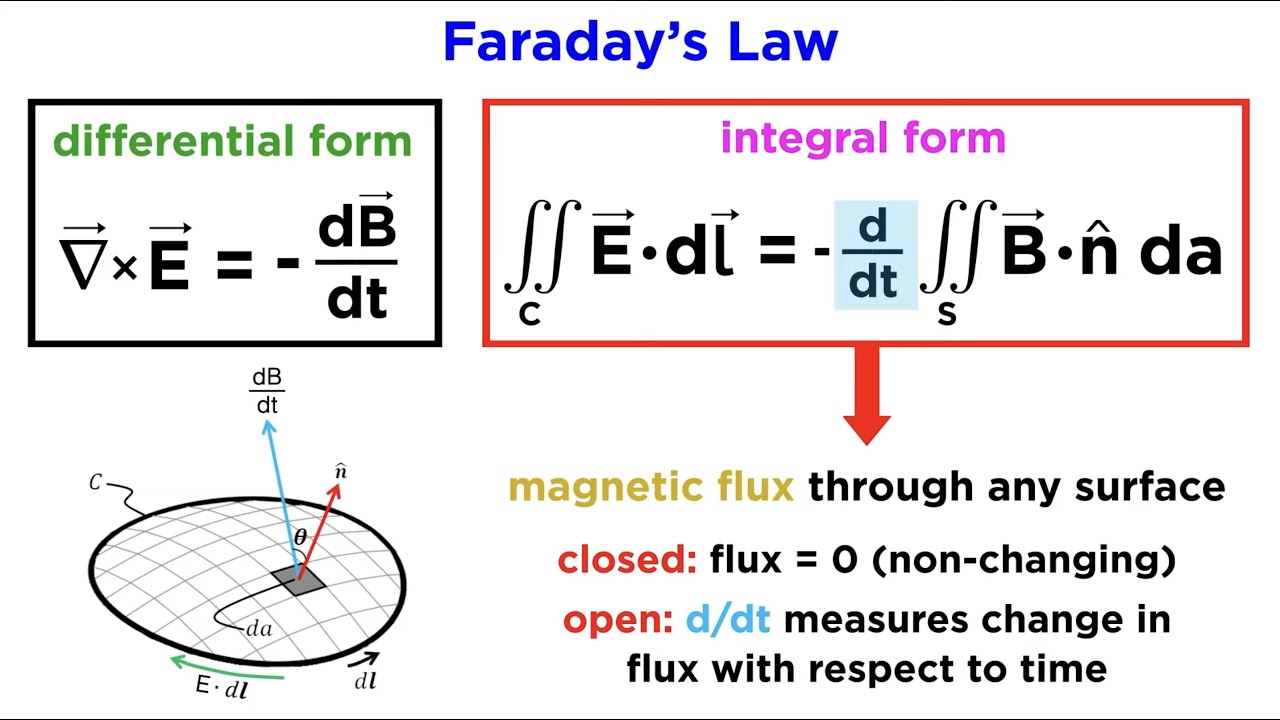
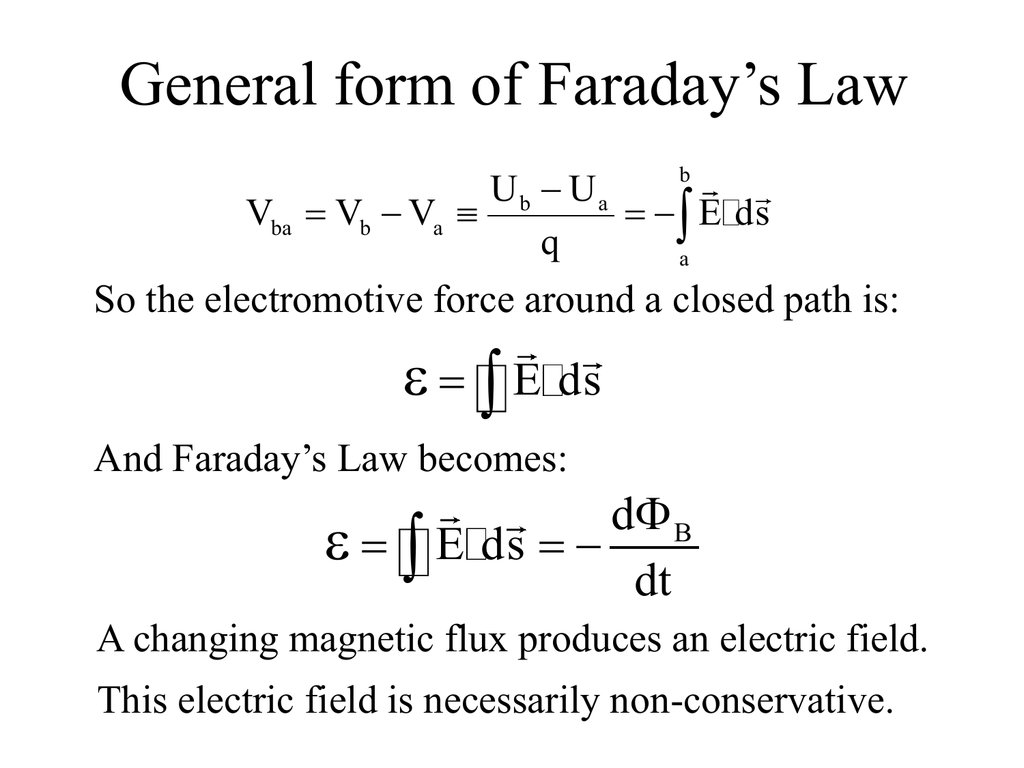
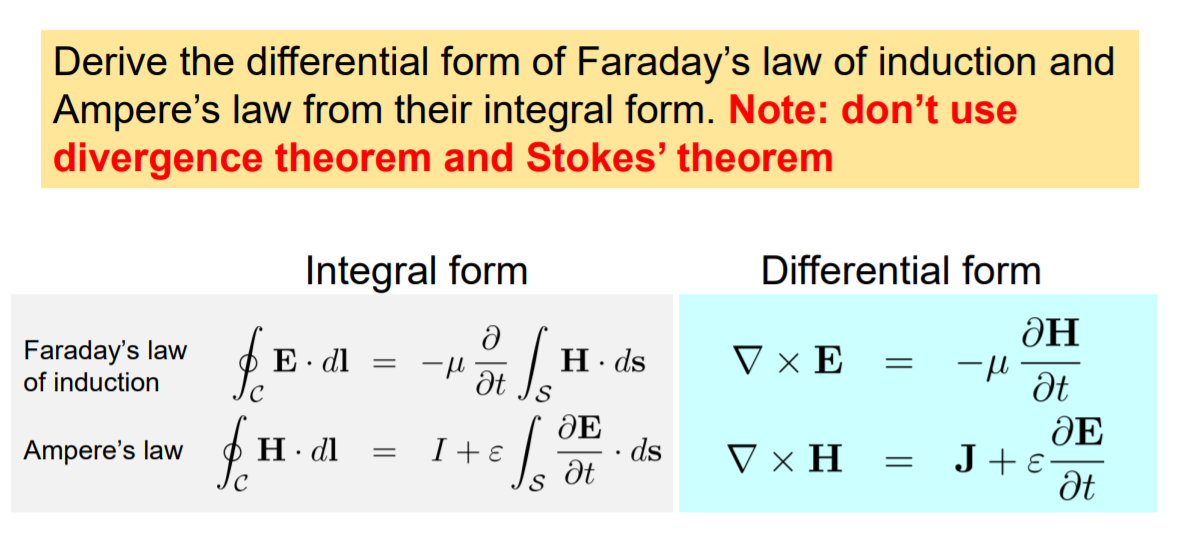
Faraday S Law Integral Form - Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Faraday’s law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism that predicts how a magnetic field will interact with an electric. Faraday’s law of induction may be stated as follows: Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of conducting material, and quantifies. The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. Using stokes’ theorem, this law can be written in integral form as \begin {equation} \label {eq:ii:17:2} \oint_\gamma\flpe\cdot d\flps=. I want to understand how stoke's theorem shows that the integral form of faraday's law:
I want to understand how stoke's theorem shows that the integral form of faraday's law: The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Using stokes’ theorem, this law can be written in integral form as \begin {equation} \label {eq:ii:17:2} \oint_\gamma\flpe\cdot d\flps=. Faraday’s law of induction may be stated as follows: Faraday’s law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism that predicts how a magnetic field will interact with an electric. Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of conducting material, and quantifies.
I want to understand how stoke's theorem shows that the integral form of faraday's law: Using stokes’ theorem, this law can be written in integral form as \begin {equation} \label {eq:ii:17:2} \oint_\gamma\flpe\cdot d\flps=. Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of conducting material, and quantifies. Faraday’s law of induction may be stated as follows: Faraday’s law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism that predicts how a magnetic field will interact with an electric. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of.
Field Integral Equation Derivation Tessshebaylo
I want to understand how stoke's theorem shows that the integral form of faraday's law: The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can.
PPT Faraday’s Law PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3607741
The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. Faraday’s law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism that predicts how a magnetic field will interact with an electric. I want to understand how stoke's theorem shows that the integral form of faraday's law: Let's consider both the integral and.
Electrical and Electronics Engineering Faraday's Law
The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of conducting material, and quantifies. Faraday’s law of induction may be stated as follows: Using stokes’ theorem, this law can be written in integral form.
Faraday's Law Understanding the Alternative (Integral Form)
Faraday’s law of induction may be stated as follows: Using stokes’ theorem, this law can be written in integral form as \begin {equation} \label {eq:ii:17:2} \oint_\gamma\flpe\cdot d\flps=. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change.
Faraday's Law Calculations
The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. I want to understand how stoke's theorem shows that the integral form of faraday's law: Using stokes’ theorem, this law can be written in integral form as \begin {equation} \label {eq:ii:17:2} \oint_\gamma\flpe\cdot d\flps=. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which.
Maxwell’s Equations Part 3 Faraday’s Law YouTube
Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of conducting material, and quantifies. I want to understand how stoke's theorem shows that the integral form of faraday's law: The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. Faraday’s law of induction may.
General form of Faraday’s Law
I want to understand how stoke's theorem shows that the integral form of faraday's law: Using stokes’ theorem, this law can be written in integral form as \begin {equation} \label {eq:ii:17:2} \oint_\gamma\flpe\cdot d\flps=. Faraday’s law of induction may be stated as follows: Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of.
Solved Derive the differential form of Faraday's law of
Faraday’s law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism that predicts how a magnetic field will interact with an electric. Faraday’s law of induction may be stated as follows: The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce.
Faraday Law, standard (integral form) Physics and mathematics
Faraday’s law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism that predicts how a magnetic field will interact with an electric. I want to understand how stoke's theorem shows that the integral form of faraday's law: Using stokes’ theorem, this law can be written in integral form as \begin {equation} \label {eq:ii:17:2} \oint_\gamma\flpe\cdot d\flps=. Faraday's law of induction explains that.
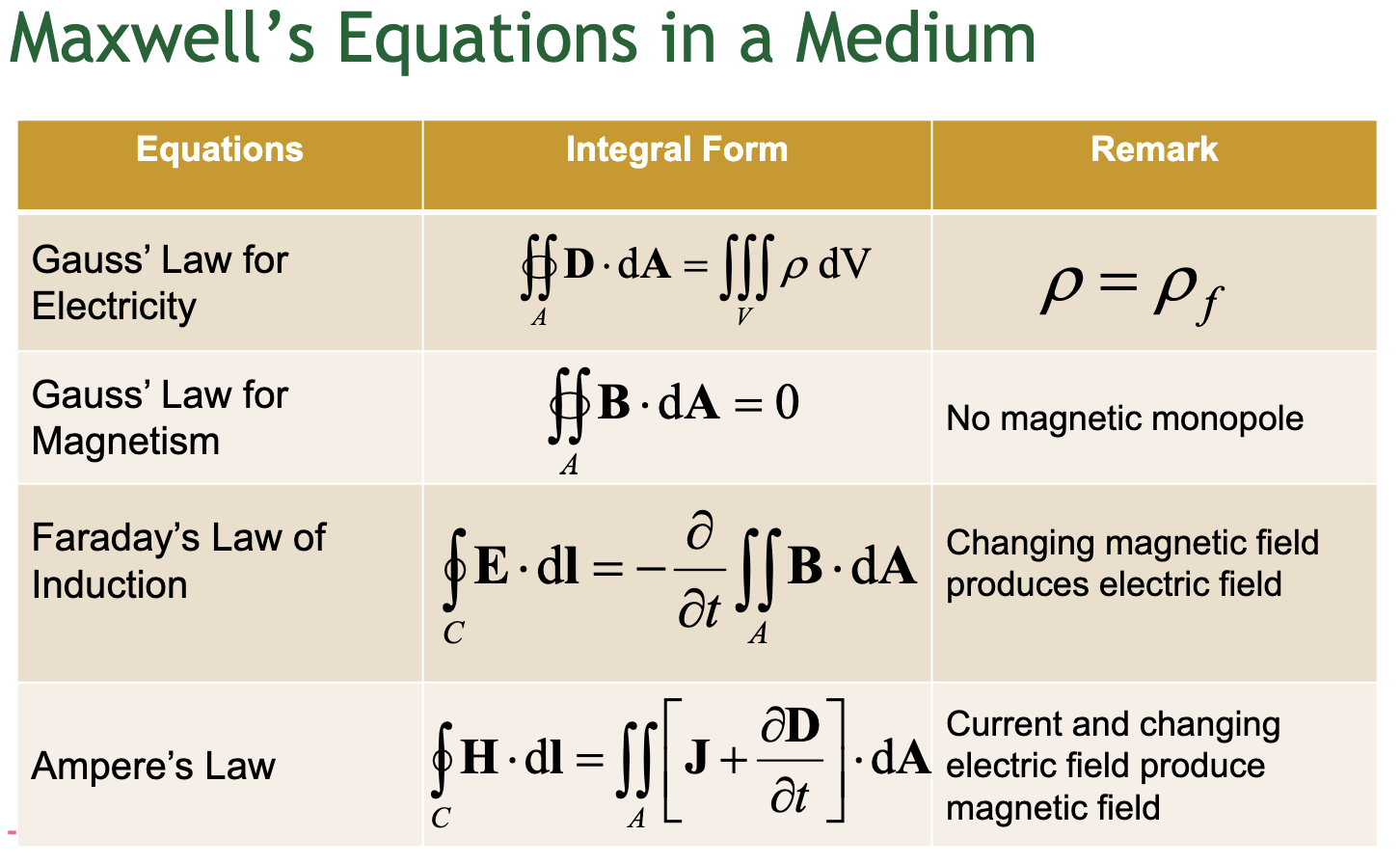
Solved Maxwell's Equations in a Medium Equations Integral
I want to understand how stoke's theorem shows that the integral form of faraday's law: Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of conducting material, and quantifies. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Faraday’s law of induction is a basic.
Faraday’s Law Of Induction May Be Stated As Follows:
Faraday’s law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism that predicts how a magnetic field will interact with an electric. The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. Using stokes’ theorem, this law can be written in integral form as \begin {equation} \label {eq:ii:17:2} \oint_\gamma\flpe\cdot d\flps=. Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of conducting material, and quantifies.
Let's Consider Both The Integral And Differential Equations Which Express The Faraday Law (3Rd Maxwell Equation):
I want to understand how stoke's theorem shows that the integral form of faraday's law: