Feature Detectors Psychology Definition
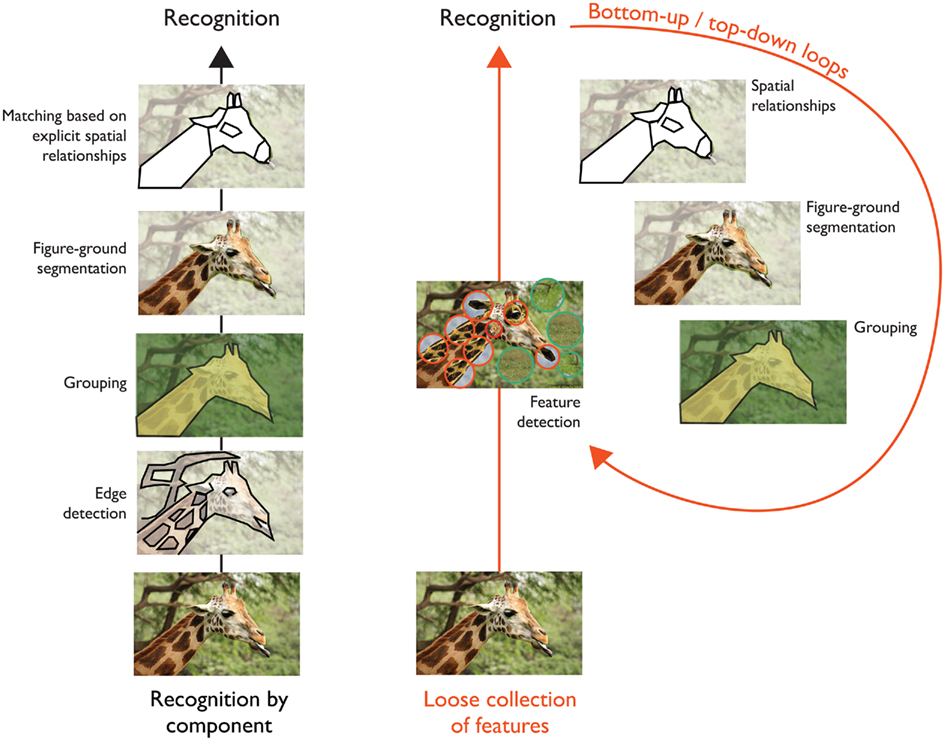
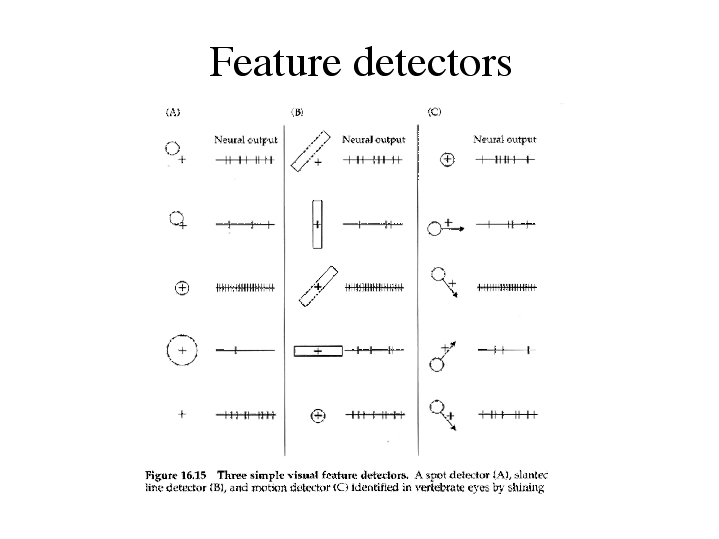
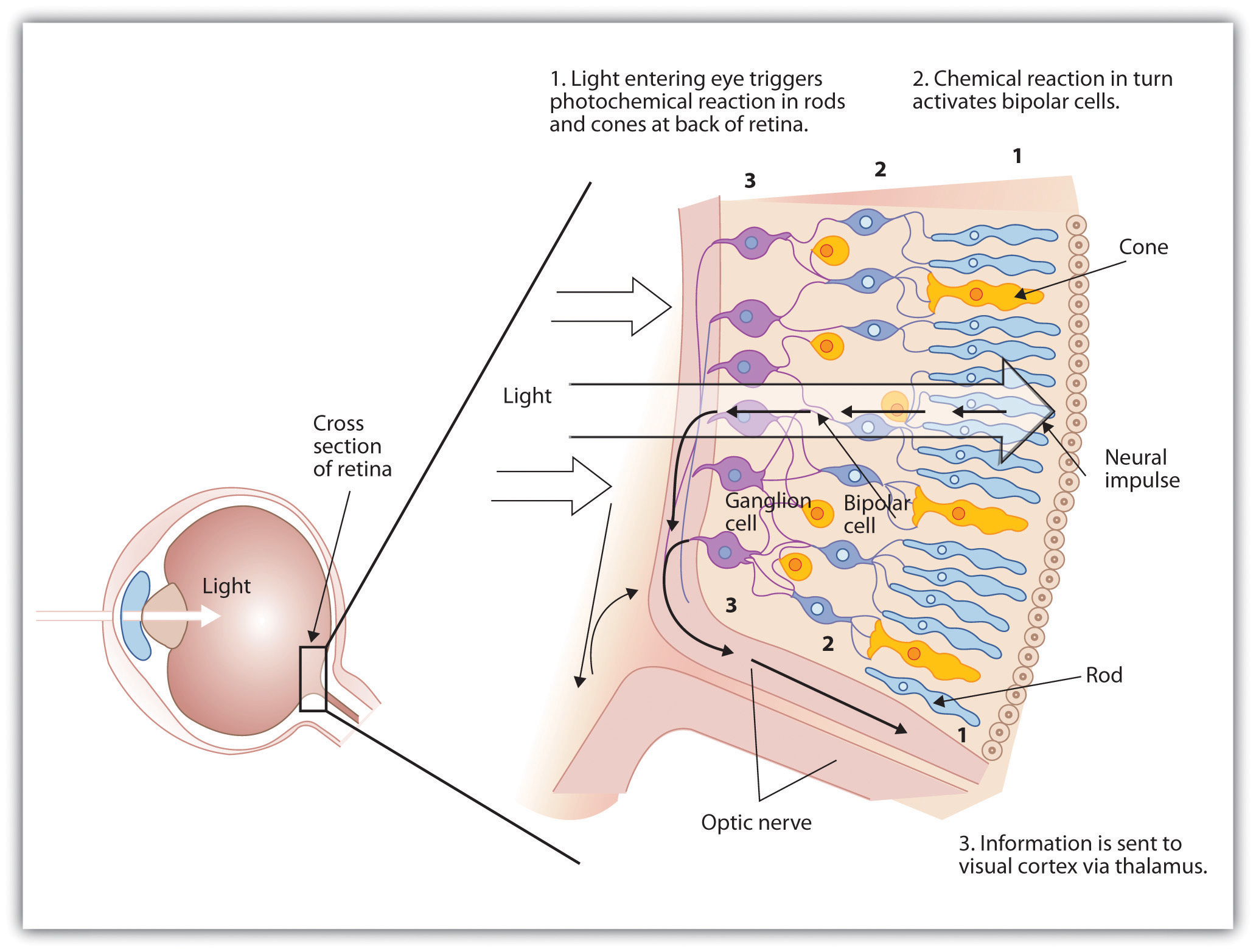
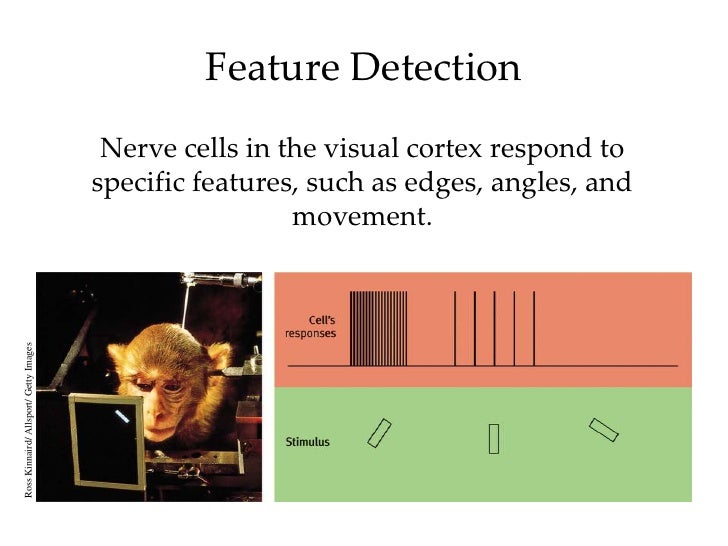
Feature Detectors Psychology Definition - Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the brain that respond to specific stimuli, such as lines, edges, shapes, or movements. The ability to detect certain types of stimuli, like movements, shape, and angles, requires specialized cells in the brain called feature. Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the visual cortex that respond to specific features of visual stimuli, such as edges, angles, or motion.
Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the brain that respond to specific stimuli, such as lines, edges, shapes, or movements. The ability to detect certain types of stimuli, like movements, shape, and angles, requires specialized cells in the brain called feature. Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the visual cortex that respond to specific features of visual stimuli, such as edges, angles, or motion.
Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the brain that respond to specific stimuli, such as lines, edges, shapes, or movements. The ability to detect certain types of stimuli, like movements, shape, and angles, requires specialized cells in the brain called feature. Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the visual cortex that respond to specific features of visual stimuli, such as edges, angles, or motion.
Vision Feature Detection & Parallel Processing YouTube
Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the brain that respond to specific stimuli, such as lines, edges, shapes, or movements. Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the visual cortex that respond to specific features of visual stimuli, such as edges, angles, or motion. The ability to detect certain types of stimuli, like movements, shape, and angles, requires specialized cells in.
Mod 14 Basic Concepts and Vision
Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the visual cortex that respond to specific features of visual stimuli, such as edges, angles, or motion. The ability to detect certain types of stimuli, like movements, shape, and angles, requires specialized cells in the brain called feature. Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the brain that respond to specific stimuli, such as lines,.
PPT The Visual System Feature Detection Model PowerPoint
Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the brain that respond to specific stimuli, such as lines, edges, shapes, or movements. Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the visual cortex that respond to specific features of visual stimuli, such as edges, angles, or motion. The ability to detect certain types of stimuli, like movements, shape, and angles, requires specialized cells in.
PPT Sensation and Perception PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the visual cortex that respond to specific features of visual stimuli, such as edges, angles, or motion. The ability to detect certain types of stimuli, like movements, shape, and angles, requires specialized cells in the brain called feature. Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the brain that respond to specific stimuli, such as lines,.
Feature Detectors Wize University Psychology Textbook Wizeprep
Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the visual cortex that respond to specific features of visual stimuli, such as edges, angles, or motion. Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the brain that respond to specific stimuli, such as lines, edges, shapes, or movements. The ability to detect certain types of stimuli, like movements, shape, and angles, requires specialized cells in.
Feature Detectors Psychology
Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the visual cortex that respond to specific features of visual stimuli, such as edges, angles, or motion. Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the brain that respond to specific stimuli, such as lines, edges, shapes, or movements. The ability to detect certain types of stimuli, like movements, shape, and angles, requires specialized cells in.
PPT Chapter 3 Neurons and Perception PowerPoint Presentation, free
Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the brain that respond to specific stimuli, such as lines, edges, shapes, or movements. The ability to detect certain types of stimuli, like movements, shape, and angles, requires specialized cells in the brain called feature. Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the visual cortex that respond to specific features of visual stimuli, such as.
Feature detectors
The ability to detect certain types of stimuli, like movements, shape, and angles, requires specialized cells in the brain called feature. Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the visual cortex that respond to specific features of visual stimuli, such as edges, angles, or motion. Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the brain that respond to specific stimuli, such as lines,.
Feature Detectors Psychology
Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the brain that respond to specific stimuli, such as lines, edges, shapes, or movements. The ability to detect certain types of stimuli, like movements, shape, and angles, requires specialized cells in the brain called feature. Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the visual cortex that respond to specific features of visual stimuli, such as.
Introductory Psychology Sensation & Perception (Vision)
Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the visual cortex that respond to specific features of visual stimuli, such as edges, angles, or motion. Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the brain that respond to specific stimuli, such as lines, edges, shapes, or movements. The ability to detect certain types of stimuli, like movements, shape, and angles, requires specialized cells in.
Feature Detectors Are Specialized Neurons In The Visual Cortex That Respond To Specific Features Of Visual Stimuli, Such As Edges, Angles, Or Motion.
The ability to detect certain types of stimuli, like movements, shape, and angles, requires specialized cells in the brain called feature. Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the brain that respond to specific stimuli, such as lines, edges, shapes, or movements.