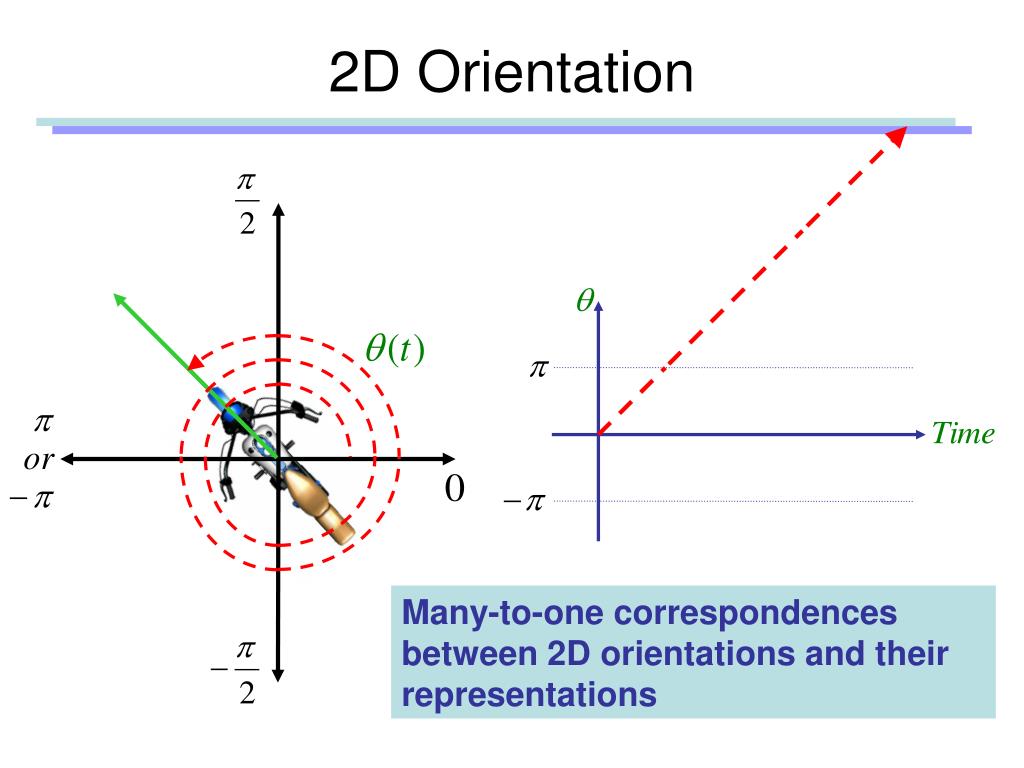
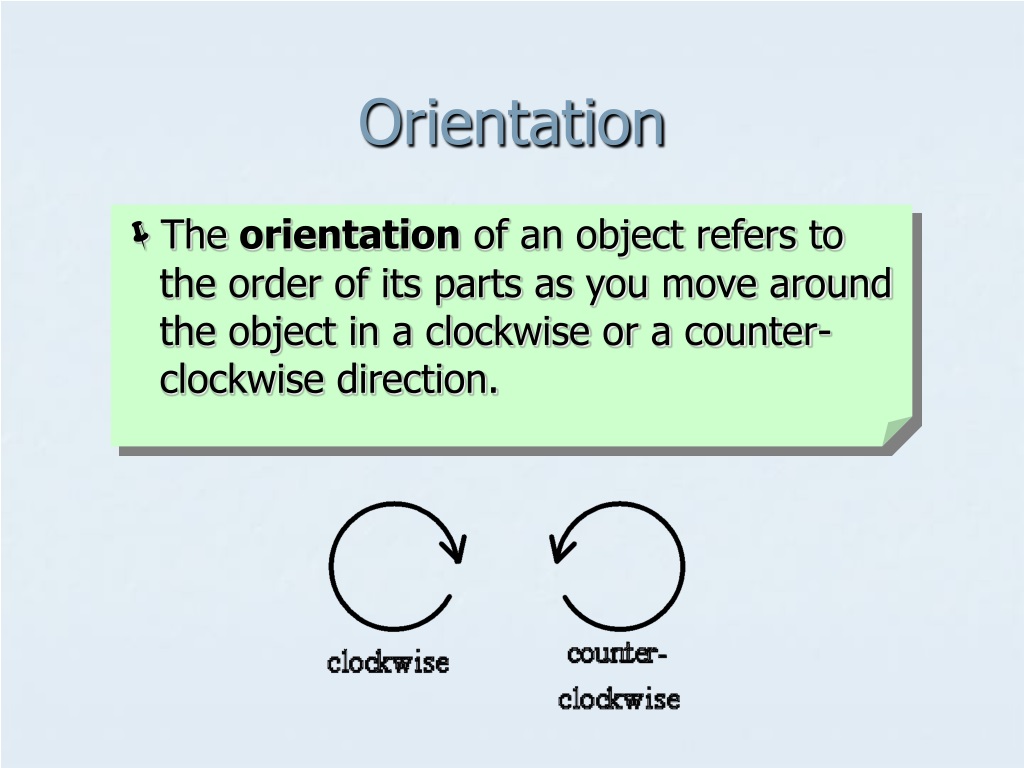
Orientation Definition In Math
Orientation Definition In Math - In classical mathematics, an orientation is the choice of an equivalence class of coordinate systems, where two coordinate. Orientation, in the context of mathematics, refers to the relative position or direction of an object or shape. It is a fundamental concept that helps us understand. An orientation is prescribed by giving an. Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. Definition 1.1 in the plane r2 an orientation defines which direction of rotation is the positive sense. What is orientation in math? Orientation in geometry refers to the direction or placement of objects or shapes in space. Orientation • the angle of an object compared to compass points or the axes of a cartesian plane.
Orientation • the angle of an object compared to compass points or the axes of a cartesian plane. Orientation, in the context of mathematics, refers to the relative position or direction of an object or shape. It is a fundamental concept that helps us understand. Definition 1.1 in the plane r2 an orientation defines which direction of rotation is the positive sense. In classical mathematics, an orientation is the choice of an equivalence class of coordinate systems, where two coordinate. Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. What is orientation in math? Orientation in geometry refers to the direction or placement of objects or shapes in space. An orientation is prescribed by giving an.
Orientation • the angle of an object compared to compass points or the axes of a cartesian plane. Definition 1.1 in the plane r2 an orientation defines which direction of rotation is the positive sense. Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. What is orientation in math? It is a fundamental concept that helps us understand. Orientation, in the context of mathematics, refers to the relative position or direction of an object or shape. Orientation in geometry refers to the direction or placement of objects or shapes in space. An orientation is prescribed by giving an. In classical mathematics, an orientation is the choice of an equivalence class of coordinate systems, where two coordinate.
Orientation Meaning
It is a fundamental concept that helps us understand. Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. What is orientation in math? Orientation • the angle of an object compared to compass points or the axes of a cartesian plane. In classical mathematics, an orientation is the choice of an equivalence.
Definition of orientation angles for a 3(2)1 Euler rotation
Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. Orientation • the angle of an object compared to compass points or the axes of a cartesian plane. It is a fundamental concept that helps us understand. In classical mathematics, an orientation is the choice of an equivalence class of coordinate systems, where.
linear algebra Orientations on Manifold Mathematics Stack Exchange
In classical mathematics, an orientation is the choice of an equivalence class of coordinate systems, where two coordinate. Definition 1.1 in the plane r2 an orientation defines which direction of rotation is the positive sense. An orientation is prescribed by giving an. Orientation in geometry refers to the direction or placement of objects or shapes in space. Orientation is the.
PPT Transformational Geometry PowerPoint Presentation, free download
What is orientation in math? Definition 1.1 in the plane r2 an orientation defines which direction of rotation is the positive sense. It is a fundamental concept that helps us understand. An orientation is prescribed by giving an. In classical mathematics, an orientation is the choice of an equivalence class of coordinate systems, where two coordinate.
Orientation 2.
In classical mathematics, an orientation is the choice of an equivalence class of coordinate systems, where two coordinate. What is orientation in math? Orientation, in the context of mathematics, refers to the relative position or direction of an object or shape. An orientation is prescribed by giving an. It is a fundamental concept that helps us understand.
Math Orientation YouTube
Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. Orientation, in the context of mathematics, refers to the relative position or direction of an object or shape. Orientation • the angle of an object compared to compass points or the axes of a cartesian plane. In classical mathematics, an orientation is the.
What is Orientation? Meaning, Importance, Best Practices
An orientation is prescribed by giving an. In classical mathematics, an orientation is the choice of an equivalence class of coordinate systems, where two coordinate. Orientation in geometry refers to the direction or placement of objects or shapes in space. Definition 1.1 in the plane r2 an orientation defines which direction of rotation is the positive sense. Orientation is the.
PPT Rotation and Orientation Fundamentals PowerPoint Presentation
It is a fundamental concept that helps us understand. Definition 1.1 in the plane r2 an orientation defines which direction of rotation is the positive sense. In classical mathematics, an orientation is the choice of an equivalence class of coordinate systems, where two coordinate. What is orientation in math? Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or.
PPT Transformational Geometry PowerPoint Presentation, free download
An orientation is prescribed by giving an. Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. Definition 1.1 in the plane r2 an orientation defines which direction of rotation is the positive sense. What is orientation in math? It is a fundamental concept that helps us understand.
PPT Motion Geometry Part I PowerPoint Presentation, free download
An orientation is prescribed by giving an. What is orientation in math? In classical mathematics, an orientation is the choice of an equivalence class of coordinate systems, where two coordinate. Orientation in geometry refers to the direction or placement of objects or shapes in space. Orientation • the angle of an object compared to compass points or the axes of.
What Is Orientation In Math?
Orientation in geometry refers to the direction or placement of objects or shapes in space. In classical mathematics, an orientation is the choice of an equivalence class of coordinate systems, where two coordinate. Definition 1.1 in the plane r2 an orientation defines which direction of rotation is the positive sense. An orientation is prescribed by giving an.
Orientation • The Angle Of An Object Compared To Compass Points Or The Axes Of A Cartesian Plane.
It is a fundamental concept that helps us understand. Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. Orientation, in the context of mathematics, refers to the relative position or direction of an object or shape.