Volumetric Heat Generation
Volumetric Heat Generation - The differential equation describing the temperature distribution can be. The volumetric heat capacity c of a soil is defined as the change in heat content of a unit bulk volume of soil per unit change in temperature. Volumetric heat generation (q''') rate is defined as the thermal power generated in the core per unit fuel volume consider an infinitesimal volume. Basic laws of heat transfer • energy balance equation describing heat input, temperature, heat transfer is similar to neutron transport equation:. The specific heat of a material is the amount of heat (joules) per unit mass (g) or mole (mol) required to raise the temperature by one degree. Uniform volumetric heat generation (q g per unit volume) within the wall.
The specific heat of a material is the amount of heat (joules) per unit mass (g) or mole (mol) required to raise the temperature by one degree. Uniform volumetric heat generation (q g per unit volume) within the wall. The volumetric heat capacity c of a soil is defined as the change in heat content of a unit bulk volume of soil per unit change in temperature. Basic laws of heat transfer • energy balance equation describing heat input, temperature, heat transfer is similar to neutron transport equation:. Volumetric heat generation (q''') rate is defined as the thermal power generated in the core per unit fuel volume consider an infinitesimal volume. The differential equation describing the temperature distribution can be.
Volumetric heat generation (q''') rate is defined as the thermal power generated in the core per unit fuel volume consider an infinitesimal volume. Basic laws of heat transfer • energy balance equation describing heat input, temperature, heat transfer is similar to neutron transport equation:. The volumetric heat capacity c of a soil is defined as the change in heat content of a unit bulk volume of soil per unit change in temperature. The differential equation describing the temperature distribution can be. The specific heat of a material is the amount of heat (joules) per unit mass (g) or mole (mol) required to raise the temperature by one degree. Uniform volumetric heat generation (q g per unit volume) within the wall.
[Case 2] Volumetric heat generation for the interface layers; (top
The differential equation describing the temperature distribution can be. Volumetric heat generation (q''') rate is defined as the thermal power generated in the core per unit fuel volume consider an infinitesimal volume. Uniform volumetric heat generation (q g per unit volume) within the wall. Basic laws of heat transfer • energy balance equation describing heat input, temperature, heat transfer is.
Volumetric Heat Generation Profile. Download Scientific Diagram
Basic laws of heat transfer • energy balance equation describing heat input, temperature, heat transfer is similar to neutron transport equation:. The specific heat of a material is the amount of heat (joules) per unit mass (g) or mole (mol) required to raise the temperature by one degree. The differential equation describing the temperature distribution can be. Volumetric heat generation.
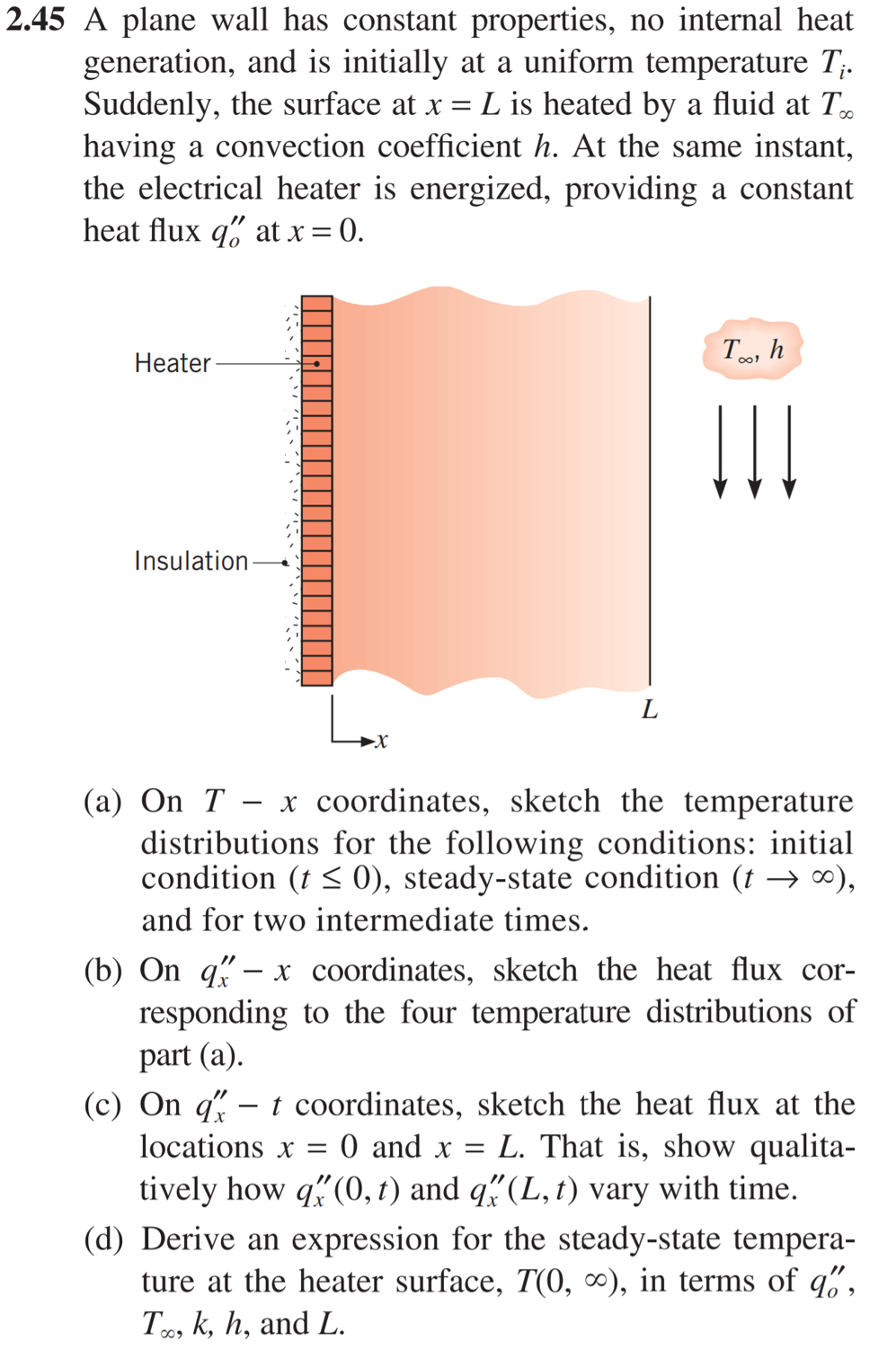
Solved 2.45 A plane wall has constant properties, no
The specific heat of a material is the amount of heat (joules) per unit mass (g) or mole (mol) required to raise the temperature by one degree. The differential equation describing the temperature distribution can be. Basic laws of heat transfer • energy balance equation describing heat input, temperature, heat transfer is similar to neutron transport equation:. Volumetric heat generation.
(PDF) Internal volumetric heat generation and heat capacity prediction
Volumetric heat generation (q''') rate is defined as the thermal power generated in the core per unit fuel volume consider an infinitesimal volume. The volumetric heat capacity c of a soil is defined as the change in heat content of a unit bulk volume of soil per unit change in temperature. Uniform volumetric heat generation (q g per unit volume).
Volumetric heat generation rate (q, W/m 3 ) profile for coil length of
Basic laws of heat transfer • energy balance equation describing heat input, temperature, heat transfer is similar to neutron transport equation:. The differential equation describing the temperature distribution can be. Volumetric heat generation (q''') rate is defined as the thermal power generated in the core per unit fuel volume consider an infinitesimal volume. The volumetric heat capacity c of a.
Solved A long cylindrical rod of diameter 200 mm with
Volumetric heat generation (q''') rate is defined as the thermal power generated in the core per unit fuel volume consider an infinitesimal volume. The differential equation describing the temperature distribution can be. Uniform volumetric heat generation (q g per unit volume) within the wall. The volumetric heat capacity c of a soil is defined as the change in heat content.
What Is The Formula Of Heat Equation Tessshebaylo
The differential equation describing the temperature distribution can be. Volumetric heat generation (q''') rate is defined as the thermal power generated in the core per unit fuel volume consider an infinitesimal volume. Uniform volumetric heat generation (q g per unit volume) within the wall. Basic laws of heat transfer • energy balance equation describing heat input, temperature, heat transfer is.
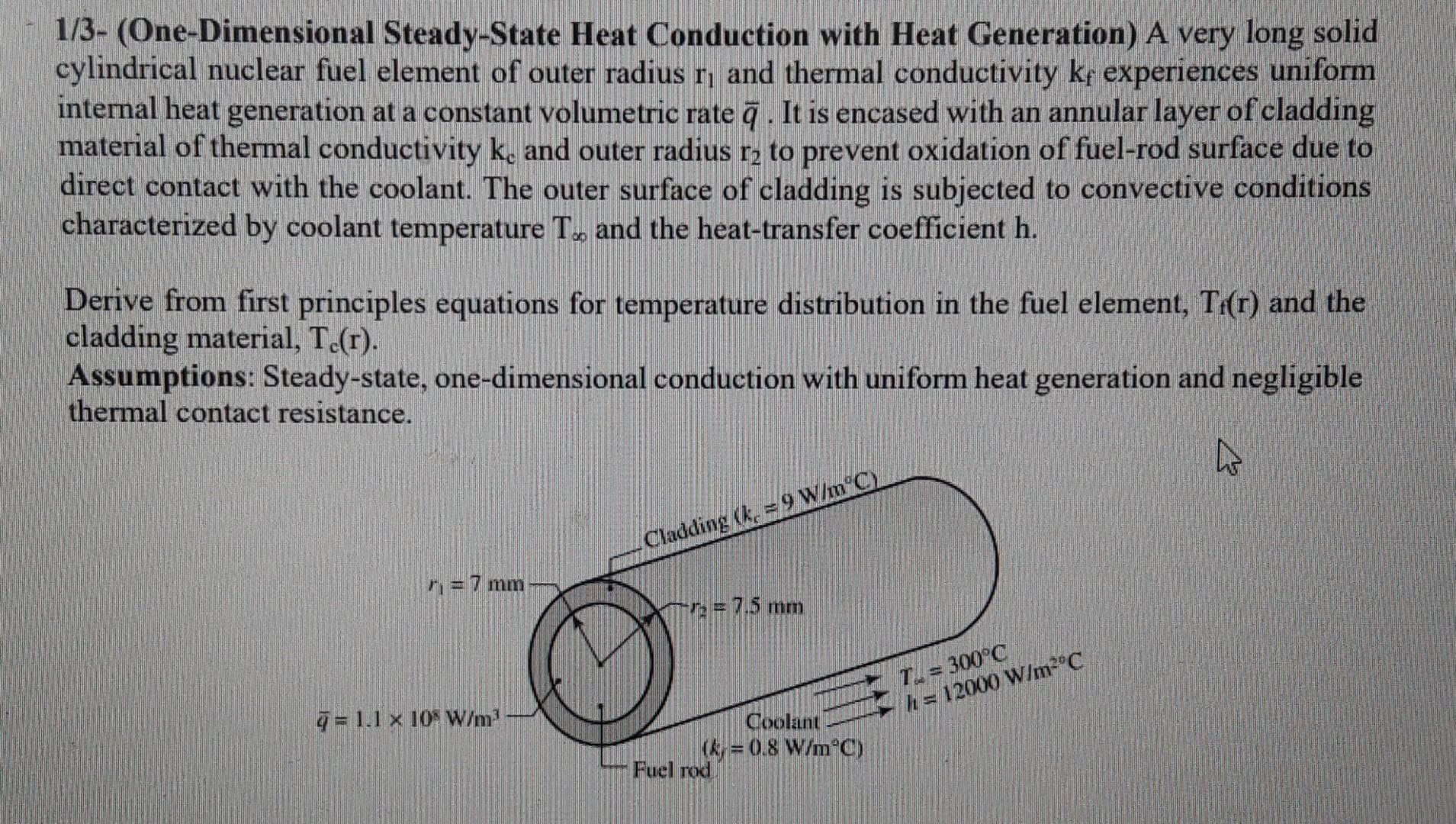
Solved 1/3 (OneDimensional SteadyState Heat Conduction
The specific heat of a material is the amount of heat (joules) per unit mass (g) or mole (mol) required to raise the temperature by one degree. Basic laws of heat transfer • energy balance equation describing heat input, temperature, heat transfer is similar to neutron transport equation:. The differential equation describing the temperature distribution can be. Uniform volumetric heat.
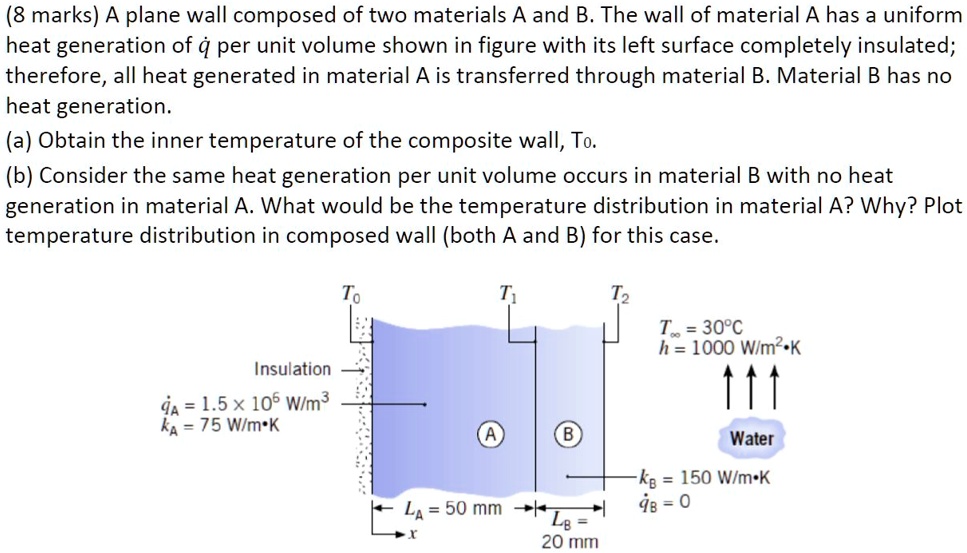
8 marks a plane wall composed of two materials a and bthe wall of
Uniform volumetric heat generation (q g per unit volume) within the wall. The specific heat of a material is the amount of heat (joules) per unit mass (g) or mole (mol) required to raise the temperature by one degree. The volumetric heat capacity c of a soil is defined as the change in heat content of a unit bulk volume.
Volumetric heat generation rate (q, W/m 3 ) profile for coil length of
Uniform volumetric heat generation (q g per unit volume) within the wall. The specific heat of a material is the amount of heat (joules) per unit mass (g) or mole (mol) required to raise the temperature by one degree. The differential equation describing the temperature distribution can be. Basic laws of heat transfer • energy balance equation describing heat input,.
Uniform Volumetric Heat Generation (Q G Per Unit Volume) Within The Wall.
The specific heat of a material is the amount of heat (joules) per unit mass (g) or mole (mol) required to raise the temperature by one degree. The differential equation describing the temperature distribution can be. The volumetric heat capacity c of a soil is defined as the change in heat content of a unit bulk volume of soil per unit change in temperature. Basic laws of heat transfer • energy balance equation describing heat input, temperature, heat transfer is similar to neutron transport equation:.
![[Case 2] Volumetric heat generation for the interface layers; (top](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Darun-Barazanchy/publication/367312100/figure/fig2/AS:11431281127642349@1679078417456/Case-2-Volumetric-heat-generation-for-the-interface-layers-top-layer-9-and-bottom.png)