What Are Exoenzymes
What Are Exoenzymes - An exoenzyme, or extracellular enzyme, is an enzyme that is secreted by a cell and functions outside that cell. Extracellular hydrolysis results from hydrolytic enzymes synthesized within and then secreted from cells. Exoenzymes and endoenzymes are both types of enzymes produced by cells, but they differ in their location and function. These enzymes are defined as. In the context of microbiology, exoenzymes are. Exoenzymes are specialised enzymes that are secreted by cells and function outside these cells.
In the context of microbiology, exoenzymes are. An exoenzyme, or extracellular enzyme, is an enzyme that is secreted by a cell and functions outside that cell. These enzymes are defined as. Exoenzymes and endoenzymes are both types of enzymes produced by cells, but they differ in their location and function. Exoenzymes are specialised enzymes that are secreted by cells and function outside these cells. Extracellular hydrolysis results from hydrolytic enzymes synthesized within and then secreted from cells.
An exoenzyme, or extracellular enzyme, is an enzyme that is secreted by a cell and functions outside that cell. These enzymes are defined as. In the context of microbiology, exoenzymes are. Exoenzymes and endoenzymes are both types of enzymes produced by cells, but they differ in their location and function. Extracellular hydrolysis results from hydrolytic enzymes synthesized within and then secreted from cells. Exoenzymes are specialised enzymes that are secreted by cells and function outside these cells.
DVC Microbiology 146 Fall 11 (Gard) Lab 14 Exoenzymes
These enzymes are defined as. Extracellular hydrolysis results from hydrolytic enzymes synthesized within and then secreted from cells. Exoenzymes are specialised enzymes that are secreted by cells and function outside these cells. Exoenzymes and endoenzymes are both types of enzymes produced by cells, but they differ in their location and function. In the context of microbiology, exoenzymes are.
Exoenzyme Alchetron, The Free Social Encyclopedia
An exoenzyme, or extracellular enzyme, is an enzyme that is secreted by a cell and functions outside that cell. Exoenzymes are specialised enzymes that are secreted by cells and function outside these cells. Extracellular hydrolysis results from hydrolytic enzymes synthesized within and then secreted from cells. These enzymes are defined as. Exoenzymes and endoenzymes are both types of enzymes produced.
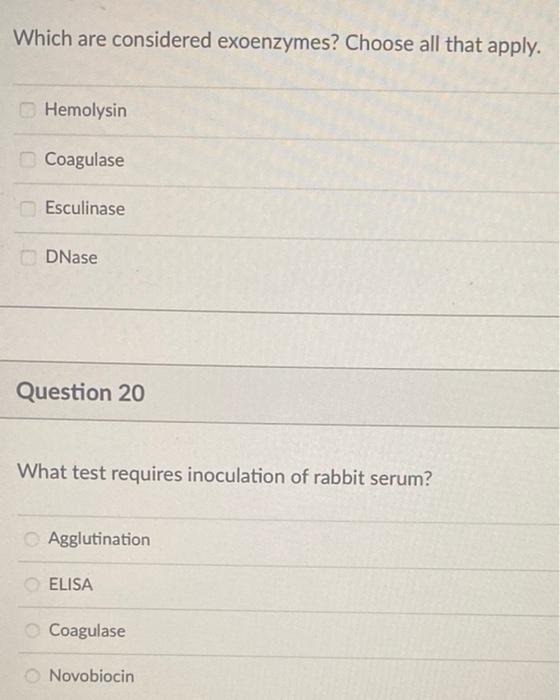
Solved Which are considered exoenzymes? Choose all that
Extracellular hydrolysis results from hydrolytic enzymes synthesized within and then secreted from cells. An exoenzyme, or extracellular enzyme, is an enzyme that is secreted by a cell and functions outside that cell. Exoenzymes are specialised enzymes that are secreted by cells and function outside these cells. Exoenzymes and endoenzymes are both types of enzymes produced by cells, but they differ.
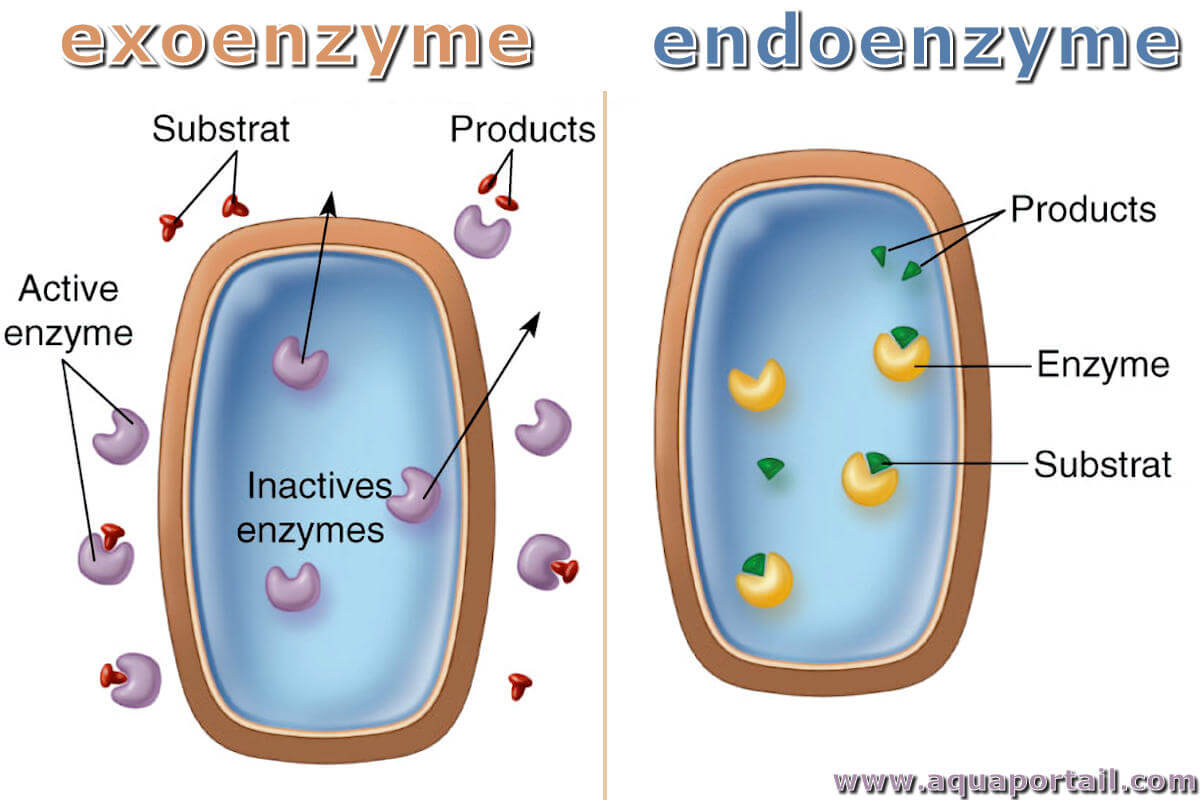
Exoenzyme vs Endoenzyme Tabular Form
Exoenzymes and endoenzymes are both types of enzymes produced by cells, but they differ in their location and function. Extracellular hydrolysis results from hydrolytic enzymes synthesized within and then secreted from cells. Exoenzymes are specialised enzymes that are secreted by cells and function outside these cells. An exoenzyme, or extracellular enzyme, is an enzyme that is secreted by a cell.
PPT Mechanism of Bacterial Damage & Bacterial Toxins PowerPoint
Extracellular hydrolysis results from hydrolytic enzymes synthesized within and then secreted from cells. Exoenzymes are specialised enzymes that are secreted by cells and function outside these cells. These enzymes are defined as. Exoenzymes and endoenzymes are both types of enzymes produced by cells, but they differ in their location and function. In the context of microbiology, exoenzymes are.
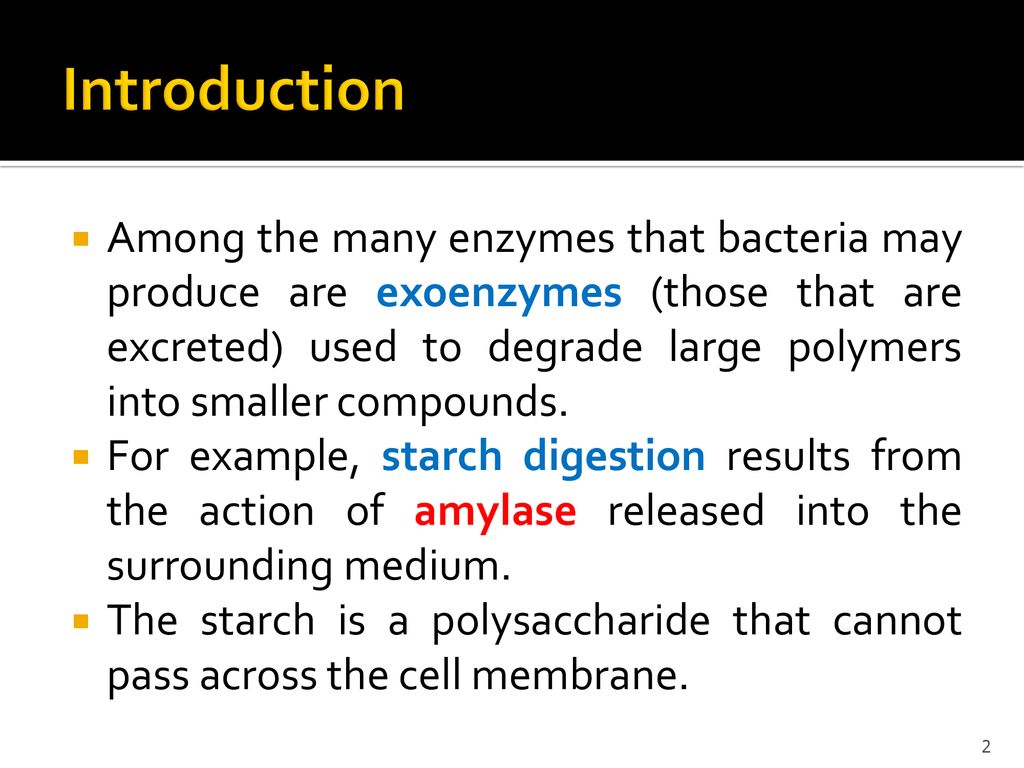
Biology & biotechnology department ppt download
Exoenzymes are specialised enzymes that are secreted by cells and function outside these cells. An exoenzyme, or extracellular enzyme, is an enzyme that is secreted by a cell and functions outside that cell. Extracellular hydrolysis results from hydrolytic enzymes synthesized within and then secreted from cells. Exoenzymes and endoenzymes are both types of enzymes produced by cells, but they differ.
(PDF) Exoenzymes as a Signature of Microbial Response to Marine
These enzymes are defined as. An exoenzyme, or extracellular enzyme, is an enzyme that is secreted by a cell and functions outside that cell. Exoenzymes and endoenzymes are both types of enzymes produced by cells, but they differ in their location and function. In the context of microbiology, exoenzymes are. Exoenzymes are specialised enzymes that are secreted by cells and.
15.3 Virulence Factors Biology LibreTexts
Exoenzymes are specialised enzymes that are secreted by cells and function outside these cells. An exoenzyme, or extracellular enzyme, is an enzyme that is secreted by a cell and functions outside that cell. Exoenzymes and endoenzymes are both types of enzymes produced by cells, but they differ in their location and function. In the context of microbiology, exoenzymes are. These.
Enzymologie définition et explications
An exoenzyme, or extracellular enzyme, is an enzyme that is secreted by a cell and functions outside that cell. In the context of microbiology, exoenzymes are. Exoenzymes and endoenzymes are both types of enzymes produced by cells, but they differ in their location and function. These enzymes are defined as. Extracellular hydrolysis results from hydrolytic enzymes synthesized within and then.
Exoenzymes 1 set up YouTube
Extracellular hydrolysis results from hydrolytic enzymes synthesized within and then secreted from cells. In the context of microbiology, exoenzymes are. Exoenzymes are specialised enzymes that are secreted by cells and function outside these cells. These enzymes are defined as. An exoenzyme, or extracellular enzyme, is an enzyme that is secreted by a cell and functions outside that cell.
Exoenzymes Are Specialised Enzymes That Are Secreted By Cells And Function Outside These Cells.
These enzymes are defined as. Exoenzymes and endoenzymes are both types of enzymes produced by cells, but they differ in their location and function. Extracellular hydrolysis results from hydrolytic enzymes synthesized within and then secreted from cells. In the context of microbiology, exoenzymes are.